
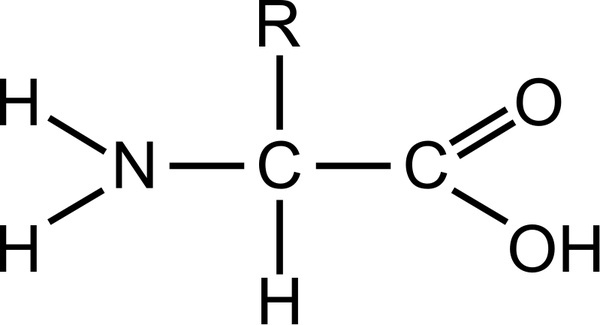
Proline is exceptional in that it has an R group that folds back and covalently bonds to the backbone of the amino acid, creating a more rigid element in a protein chain that reduces free movement of the polypeptide chain. The small R groups here are more readily packed into tight formations. In proteins that embed themselves into or through membranes, these amino acids can orient themselves toward hydrophobic portions of the inside of the membrane. When incorporated into globular proteins they tend to pack inward among other hydrophobic groups. The amino acids in this group have nonpolar, hydrophobic R groups. Instead, with only very minor exceptions, every amino acid found in cells and in proteins is in the L configuration. Nature has not distributed the stereoisomers of amino acids equally. The designations used in organic chemistry are not generally applied to amino acid nomenclature, but a similar system uses L and D to describe these enantiomers. With the exception of glycine, which has an R-group consisting of a hydrogen atom, all of the amino acids in proteins have four different groups attached to them and consequently can exist in two mirror isomeric forms. The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino groups are common to all amino acids, so the R-group is the only variable feature. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups – a hydrogen, a carboxylic acid group, an amine group, and an R-group, sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain. “It is one of the more striking generalizations of biochemistry …that the twenty amino acids and the four bases, are, with minor reservations, the same throughout Nature.” – Francis CrickĪll amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in Figure 2.1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
